Periodontology (Gum Disease)
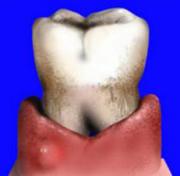
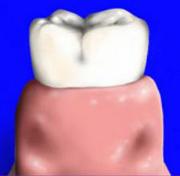 What are the signs for a healthy gum?
What are the signs for a healthy gum?
- Is light pink in colour (darker for people with darker complexions) stippled, much like the surface of an orange ,
- Don’t bleed when brushing or flossing
- Is not tender or swollen
- Is firmly attached to tooth and bone
- Healthy gingiva has a smooth or scalloped appearance around each tooth.
- Healthy gingiva fills and fits each interdental space
- Healthy gums hold tight to each tooth in that the gingival surface narrows to “knife-edge” thin at the free gingival margin
- Follow the contours of the dental cervical
Dental plaque is a biofilm (usually colorless) that builds up on the teeth If not removed regularly, it can lead to caries or gum diseases
The microorganisms present in dental plaque are all naturally present in the oral cavity, and are normally harmless. However, failure to remove plaque by regular toothbrushing means that they are allowed to build up in a thick layer. Those microorganisms nearest the tooth surface convert to anaerobic respiration; it is in this state that they start to produce acids.
- Acids released from dental plaque lead to demineralization of the adjacent tooth surface, and consequently to dental caries. Saliva is also unable to penetrate the build-up of plaque and thus cannot act to neutralize the acid produced by the bacteria and remineralize the tooth surface.
- They also cause irritation of the gums around the teeth that could lead to gingivitis, periodontal disease and tooth loss.
- Plaque build up can also become mineralized and form calculus (tartar).
The first sign of a gingival inflamation is the bleeding,which is followed by bad breath and changes in colour and shape of the gingiva.Tooth loss due to gingival inflamations are superior in number to those of dental caries.
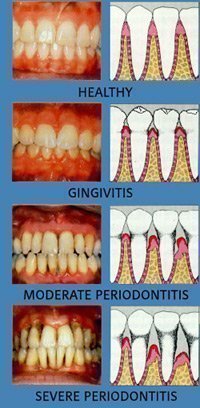 Signs of periodontal diseases
Signs of periodontal diseases
- First and the most important sign is gingival bleeding.Healthy gum doesn’t bleed.
- Redness and swelling of the gum
- Recessions of the gum and sensitivity at root surfaces accompanying it.
- Black areas at gingival margins or at interdental areas due to tartar.
- If pus is coming through the gum and tooth interface
- If teeth beginn to lenghten and become loose and spaces created between the teeth
- If bad breath and bad taste exists then without being late one has to visit a dentist
Etiology of the periodontal disease:
The primary etiology, or cause, of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene which leads to the accumulation of a bacterial matrix at the gum line, called dental plaque. You can scratch it down with your fingernail.In one miligram of the plaque there arebetween 200-50 million bacteria. Apart from this you will find below the other factors that contribute to periodontal health.
- Genetic Factors: A very strong risk factor is one’s genetic susceptibility.Research has shown that it makes up %30 of the cases.The poor oral hygiene increases the possibility of the periodontal disease up to 6 times.People with a family history of periodontal disease have to go for a check up to a specialist..
- Smoking:As we all know smoking causes diseases such as cancer ,heart disease.It should be noted that smoking also contributes to periodontal diseases and oral lesions.The significance of all of the research is that the presence of gum disease is highest for smokers, next highest for ex-smokers and lowest for those people who had never smoked. It has also been shown that former smokers and those who had never smoked did, in fact, respond better to the treatment of gum disease than did those people who did still smoke. It can be concluded that those periodontal patients who stop smoking will have a better chance of being successful with the periodontal therapy that is indicated for their case.
- Medication: Some drugs, such as oral contraceptives, anti-depressants, and certain heart medicines, can affect your oral health. Just as you notify your pharmacist and other health care providers of all medicines you are taking and any changes in your overall health, you should also inform your dental care provider. For example researchers found that prolonged use of anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS) is closely associated with significant levels of gingival enlargement, according to a new study. Amother example is the problem with bisphosphonates:It is counter-intuitive to believe that bone-sparing drugs such as IV bisphosphonates can have the opposite affect and actually necrotize the jaw bonesys the latest research. A last but a very common medication problem related to peridontal tissues is adresses in a study released in the Journal of Periodontology suggesting that frequent dental visits following initial periodontal treatment may significantly reduce gingival overgrowth in patients taking nifedipine, a commonly prescribed medication for high blood pressure
- Hormonal changes: A woman’s health needs are unique. Though brushing and flossing daily, a healthy diet, and regular exercise are important for oral health throughout life, there are certain times in a woman’s life when extra care is needed—times when you mature and change such as puberty or menopause, and times when you have special health needs, such as menstruation or pregnancy. During these particular times, a woman’s body experiences hormonal changes that can affect many of the tissues in your body, including the gums. Your gums can become sensitive, and at times react strongly to the hormonal fluctuations. This may make you more susceptible to gum disease. Additionally, recent studies suggest that pregnant women with gum disease are seven times more likely to deliver preterm, low birth weight babies.
- Stress: Is a risk factor for periodontal disease.Stress is linked to many serious conditions such as hypertension, cancer, and numerous other health problems. Research demonstrates that stress can make it more difficult for the body to fight off infection, including periodontal diseases.
- Clenching or grinding: Clenching or grinding your teeth can put excess force on the supporting tissues of the teeth and could speed up the rate at which these periodontal tissues are destroyed.To stop this clenching and grinding is one of the major issues that has to be solved by protection therapies such as wearing night guards during sleep .
- Poor nutrition : A diet low in important nutrients can compromise the body’s immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infection. Because periodontal disease is a serious infection, poor nutrition can worsen the condition of your gums.
- Diabet – Şeker Hastalığı: Diabet hastaları periodontal (diş eti) enfeksiyon açısından yüksek risk grubuna girerler. Mutlaka rutin diş eti kontrollerini bir diş eti uzmanına (periodontolog) yaptırarak ağız hijyenlerine ayrıca özen göstermelidirler.
- Kötü Yapılmış Kuron, Köprü ve Dolgular: Dişetine basan ve taşkın yapılmış dolgu, kuron ve köprüler dişetlerinde problem oluştuturur.
What are the different peridontal diseases?
Gingivitis
Is the mildest form of periodontal disease. It causes the gums to become red, swollen, and bleed easily. There is usually little or no discomfort at this stage. Gingivitis is often caused by inadequate oral hygiene. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and good oral home care.If not treated it may convert to a more serious periodontal problem
Cronic Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. With time, plaque can spread and grow below the gum line. Toxins produced by the bacteria in plaque irritate the gums. The toxins stimulate a chronic inflammatory response in which the body in essence turns on itself, and the tissues and bone that support the teeth are broken down and destroyed. Gums separate from the teeth, forming pockets (spaces between the teeth and gums) that become infected. As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. Often, this destructive process has very mild symptoms. Eventually, teeth can become loose and may have to be removed.This is one of the most frequently observed type of periodontitis. Although it is often seen at adults it may also be encountered at different ages. The atachment loss is generally slow but progressive periods may also be witnessed.
Agressive Periodontitis
It occurs in patients who are otherwise clinically healthy. Common features include rapid attachment loss and bone destruction and familial aggregation.Sometimes the respond to peripdontal procedures are vey poor and most of the time they have to be supported with antimicrobial therapy.
Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic disease
Often begins at a young age. Systemic conditions such as heart disease, respiratory disease, and diabetes are associated with this form of periodontitis.
Necrotizing Periodontitis
Is an infection characterized by necrosis of gingival tissues, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. These lesions are most commonly observed in individuals with systemic conditions such as HIV infection, malnutrition and immunosuppression.
What is the treatment for peridontal disease?
Following are some of the procedures that periodontists use to treat patients diagnosed with a periodontal (gum) disease. The main cause of periodontal disease is bacteria in the form of a sticky, colorless plaque that constantly forms on your teeth; however, many other factors can cause periodontal (gum) disease or influence its progression.
Non-Surgical Treatments
AAP treatment guidelines stress that periodontal health should be achieved in the least invasive and most cost-effective manner. This is often accomplished through non-surgical periodontal treatment, including scaling and root planing (a careful cleaning of the root surfaces to remove plaque and calculus [tartar] from deep periodontal pockets and to smooth the tooth root to remove bacterial toxins), followed by adjunctive therapy such as local delivery antimicrobials and host modulation, as needed on a case-by-case basis.
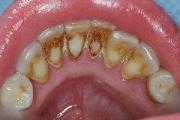
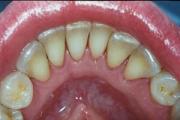
Most periodontists would agree that after scaling and root planing, many patients do not require any further active treatment, including surgical therapy. However, the majority of patients will require ongoing maintenance therapy to sustain health. Non-surgical therapy does have its limitations, however, and when it does not achieve periodontal health, surgery may be indicated to restore periodontal anatomy damaged by periodontal diseases and to facilitate oral hygiene practices.
Periodontal Surgery
If you’re diagnosed with periodontal disease, your periodontist may recommend periodontal surgery. Periodontal surgery is necessary when your periodontist determines that the tissue around your teeth is unhealthy and cannot be repaired with non-surgical treatment. Following are the four types of surgical treatments most commonly prescribed:
- Pocket reduction procedures:Your bone and gum tissue should fit snugly around your teeth like a turtleneck around your neck. When you have periodontal disease, this supporting tissue and bone is destroyed, forming “pockets” around the teeth.Over time, these pockets become deeper, providing a larger space for bacteria to live. As bacteria develop around the teeth, they can accumulate and advance under the gum tissue. These deep pockets collect even more bacteria, resulting in further bone and tissue loss. Eventually, if too much bone is lost, the teeth will need to be extracted.Your periodontist has measured the depth of your pocket(s). A pocket reduction procedure has been recommended because you have pockets that are too deep to clean with daily at-home oral hygiene and a professional care routine.During this procedure, your periodontist folds back the gum tissue and removes the disease-causing bacteria before securing the tissue into place. In some cases, irregular surfaces of the damaged bone are smoothed to limit areas where disease-causing bacteria can hide. This allows the gum tissue to better reattach to healthy bone. Reducing pocket depth and eliminating existing bacteria are important to prevent damage caused by the progression of periodontal disease and to help you maintain a healthy smile. Eliminating bacteria alone may not be sufficient to prevent disease recurrence. Deeper pockets are more difficult for you and your dental care professional to clean, so it’s important for you to reduce them. Reduced pockets and a combination of daily oral hygiene and professional maintenance care increase your chances of keeping your natural teeth – and decrease the chance of serious health problems associated with periodontal disease.
- Regenerative Procedures:Your periodontist may recommend a regenerative procedure when the bone supporting your teeth has been destroyed. These procedures can reverse some of the damage by regenerating lost bone and tissue.During this procedure, your periodontist folds back the gum tissue and removes the disease-causing bacteria. Membranes (filters), bone grafts or tissue-stimulating proteins can be used to encourage your body’s natural ability to regenerate bone and tissue. There are many options to enhance support for your teeth and to restore your bone to a healthy level. Your periodontist will discuss your best options with you. Eliminating existing bacteria and regenerating bone and tissue helps to reduce pocket depth and repair damage caused by the progression of periodontal disease. With a combination of daily oral hygiene and professional maintenance care, you’ll increase the chances of keeping your natural teeth – and decrease the chances of serious health problems associated with periodontal disease.
- Crown Lengthening :
Periodontal procedures are available to lay the groundwork for restorative and cosmetic dentistry and/or to improve the esthetics of your gum line.You may have asked your periodontist about procedures to improve a “gummy” smile because your teeth appear short. Your teeth may actually be the proper lengths, but they’re covered with too much gum tissue. To correct this, your periodontist performs crown lengthening.During this procedure, excess gum and bone tissue is reshaped to expose more of the natural tooth. This can be done to one tooth, to even your gum line, or to several teeth to expose a natural, broad smile. Your dentist or periodontist may also recommend crown lengthening to make a restorative or cosmetic dental procedure possible. Perhaps your tooth is decayed, broken below the gum line, or has insufficient tooth structure for a restoration, such as a crown or bridge. Crown lengthening adjusts the gum and bone level to expose more of the tooth so it can be restored. Whether you have crown lengthening to improve function or esthetics, patients often receive the benefits of both: a beautiful new smile and improved periodontal health – your keys to smiling, eating and speaking with comfort and confidence.
- Soft Tissue grafts:
Periodontal procedures are available to stop further dental problems and gum recession, and/or to improve the esthetics of your gum line. Exposed tooth roots are the result of gum recession. Perhaps you wish to enhance your smile by covering one or more of these roots that make your teeth appear too long. Or, maybe you’re not bothered by the appearance of these areas, but you cringe because the exposed roots are sensitive to hot or cold foods and liquids.Your gums may have receded for a variety of reasons, including aggressive tooth brushing or periodontal disease. You may not be in control of what caused the recession, but prior to treatment your periodontist can help you identify the factors contributing to the problem. Once these contributing factors are controlled, a soft tissue graft procedure will repair the defect and help to prevent additional recession and bone loss.
- Hard Tissue grafts:
During peridontal precedures the bone uderlying the reflected gum tissue may need some additional bone graftind due to severe resorbtion which can be either compansated with autologous bone harvested from one owns bone or with hard tiisue grafts in form of blocks or bone granules from tissue banks
- Cosmetic gingival surgery:
The first thing to consider when establishing a beautiful harmonic smile is to pay attention to the harmony between teeth and gums. The amount of gum we show during smile has a big impact on the appearance of the teeth. Asymetrical gingival margins give the impression of irregular teeth and a noneven smile. If the gums receed than the teeth look longer than they are.To fix the problem we need some cosmetic gingival surgeries.
- Gummy Smile: People who are dissatisfied with their smile due to exessive gum tissue display may have their gingival margins recontoured with a little surgical procedure to have better proportinated gum and dental tissues which will look nicer,even if the patient does not undergo any other cosmetic restorative work done with his teeth.
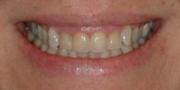
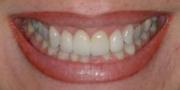
- Gum Recession: The result of some recessions are too long teeth with roots exposed and hypersensitivity present. In those situations with minor surgical procedures soft tissue can be grated to that site to cover the exposed site,to have better esthetics and to prevent further hypersensitivity.
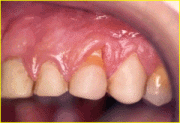
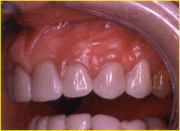
- Irregular gum margins:Gums that frame the teeth may be located sometimes too high sometimes too low depending on many factors sıch as recessions,defects from tooth loss,eruption problems.Before proceeding with the esthetic procedures the gum margins have to be put in ideal position and in harmony with the teeth.
- Gum pigmentation: Due to trauma or congenitally gum tissues may have differently pigmented areas.If they are in the smile frame they have to be removed somehow.
How can you avoid the peridontal problems?
 You can play an important role in preventing periodontal diseases. To keep your teeth you have to remove plaque by brushing,flossing and rinsing with antibacterial agents every day.Periodontal hastalıkların önlenmesinde önemli rol oynayabilirsiniz.
You can play an important role in preventing periodontal diseases. To keep your teeth you have to remove plaque by brushing,flossing and rinsing with antibacterial agents every day.Periodontal hastalıkların önlenmesinde önemli rol oynayabilirsiniz.
 In addition to what is mentioned above minimum 2 times a year to visit your dentist and have your regular check-ups done is also essential.Regular oral hygiene and to refrain from sticky foods help to reduce plaque and tartar but doesn’t solve the problem radically.To help it you need to have your teeth cleaned especially the areas you can not reach with professional care.by your dentist.And according to your needs the program that your dentist will put up is going tto be the guidelines you have to follow for aproper oral hygiene.
In addition to what is mentioned above minimum 2 times a year to visit your dentist and have your regular check-ups done is also essential.Regular oral hygiene and to refrain from sticky foods help to reduce plaque and tartar but doesn’t solve the problem radically.To help it you need to have your teeth cleaned especially the areas you can not reach with professional care.by your dentist.And according to your needs the program that your dentist will put up is going tto be the guidelines you have to follow for aproper oral hygiene.
